The Inner Workings of DHCP: Explained for Beginners
1. Introduction to DHCP Protocol
2. How DHCP Works
• DHCP Discover
• DHCP Offer
• DHCP Request
• DHCP Acknowledgment
3. Benefits of DHCP Protocol
• Simplified Network Configuration
• Efficient IP Address Management
• Dynamic Host Configuration
4. DHCP Options
• IP Address Lease Time
• Default Gateway
• DNS Server
5. DHCP Relay Agents
6. DHCPv4: DHCP for IPv4 and IPv6
7. DHCP Security Considerations
• DHCP Snooping
• DHCP Starvation Attacks
8. DHCP Configurations
9. Conclusion
10. FAQs
Introduction to DHCP Protocol
It is known as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or sometimes called as BOOTP Protocol, This maks easier to allocate and manage IP addresses in a network. Let find out more regarding the DHCP Protocol. It works in port 67 and 68 i.e Capture only traffic to and from ports 67 and 68:
How DHCP Works :
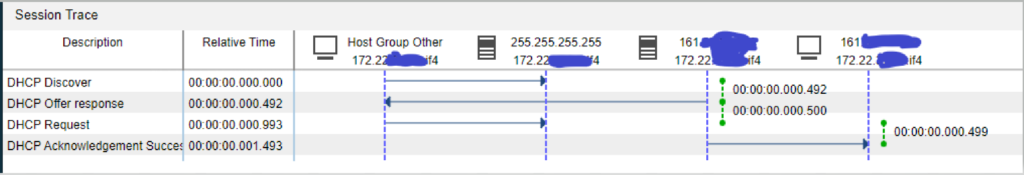
The DHCP protocol operates based on a client-server model, where the DHCP server dynamically assigns IP addresses and other network parameters to clients requesting them. The process involves four key steps: DHCP Discover, DHCP Offer, DHCP Request, and DHCP Acknowledgment.
It mostly runs on UDP.
DHCP Discover: When a client device connects to a network, it sends a DHCP Discover message as a broadcast. This message seeks a DHCP server that can provide the necessary network configuration.
DHCP Offer: Upon receiving the DHCP Discover message, a DHCP server responds with a DHCP Offer message. This message contains the IP address, lease time, and other configuration parameters that the server is willing to assign to the client.
DHCP Request: The client, upon receiving multiple DHCP Offer messages, selects one and sends a DHCP Request message to the chosen DHCP server, confirming the acceptance of the offered configuration.
DHCP Acknowledgment: The DHCP server responds with a DHCP Acknowledgment message, confirming the successful allocation of the requested network configuration to the client.

Different Devices can get IP from Server
More Messages can be found in the trace files:
Dhcp Decline: If provided IP conflicts client sends a decline message.
DHCP NACK: Server may also respond with NACK message saying offer is no longer valid.
DHCP Release: A DHCP Release message is sent by a DHCP client to release its IP address. After receiving a DHCP Release message, the DHCP server can allocate this IP address to another DHCP client.
DHCP Inform: The client ends the lease by sending a DHCPRELEASE message to the DHCP server. The server will then return the client’s IP address to the available address pool.
When the client doesnot get any IP from server in windows it will assign a dummy IP 169.xxx.xxx.xxx .
Real Time Traffic Flow:

Benefits of DHCP Protocol
The DHCP protocol brings several advantages to network administrators and users alike:
It assign IP in very less time.
Simplified Network Configuration: With DHCP, network administrators can easily manage and distribute IP addresses and other configuration parameters to connected devices. Manual configuration becomes unnecessary, saving time and effort.
Efficient IP Address Management: DHCP allows for the dynamic allocation of IP addresses. It ensures that addresses are assigned only when needed and automatically releases them when they are no longer in use, optimizing address space utilization.
Dynamic Host Configuration: DHCP enables devices to obtain updated network parameters, such as DNS server information and default gateway, automatically. This dynamic nature ensures that devices always have the most up-to-date configuration.
DHCP Options
DHCP provides various options that can be included in the DHCP messages to further customize the network configuration. Some common options include:
1. IP Address Lease Time: This option specifies the duration for which an IP address is valid for a client. After the lease time expires, the client must renew its lease with the DHCP server.
2. Default Gateway: The default gateway option informs the client about the IP address of the router that serves as the gateway to access other networks or the internet.
3. DNS Server: DHCP can provide the IP address of the DNS server, which is crucial for resolving domain names.The DNS server option ensures that clients can perform DNS lookups and translate domain names into IP addresses, allowing seamless communication across the internet.
DHCP Relay Agents
In larger networks with multiple subnets, DHCP relay agents play a significant role in facilitating the DHCP process. These agents receive DHCP messages from clients on one subnet and forward them to the DHCP server located on a different subnet. This allows DHCP requests and responses to traverse between subnets, enabling centralized DHCP management while maintaining efficient network configuration.
Is DHCP used for IPv4 or IPv6?
YES, DHCP works for both IPv4 and IPv6.
In IPv4 below address are given to assign DHCP address in a network.
Class A: 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
Class B: 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
Class C: 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
Also in IPv6 its functionality has been extended to support IPv6 with the introduction of DHCPv6. DHCPv6 performs similar functions to DHCP but focuses on providing network configuration for IPv6 addresses. With the widespread adoption of IPv6, DHCPv6 plays a vital role in simplifying the assignment of IPv6 addresses and other network parameters in modern networks.
IPv6 Private address which can be used for assigning IP address in a network: FD00::/7
DHCP Security Considerations
While DHCP offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to consider security aspects to safeguard the network against potential threats. Two common security considerations are DHCP snooping and DHCP starvation attacks.
DHCP Snooping: DHCP snooping is a feature implemented on switches to prevent unauthorized DHCP servers from distributing network configuration. It ensures that only trusted DHCP servers can respond to client requests, mitigating the risk of rogue DHCP servers compromising the network.
DHCP Starvation Attacks: DHCP starvation attacks aim to exhaust the available IP address pool by overwhelming the DHCP server with a barrage of invalid requests. Implementing appropriate security measures, such as rate limiting and DHCP server hardening, helps protect against such attacks.
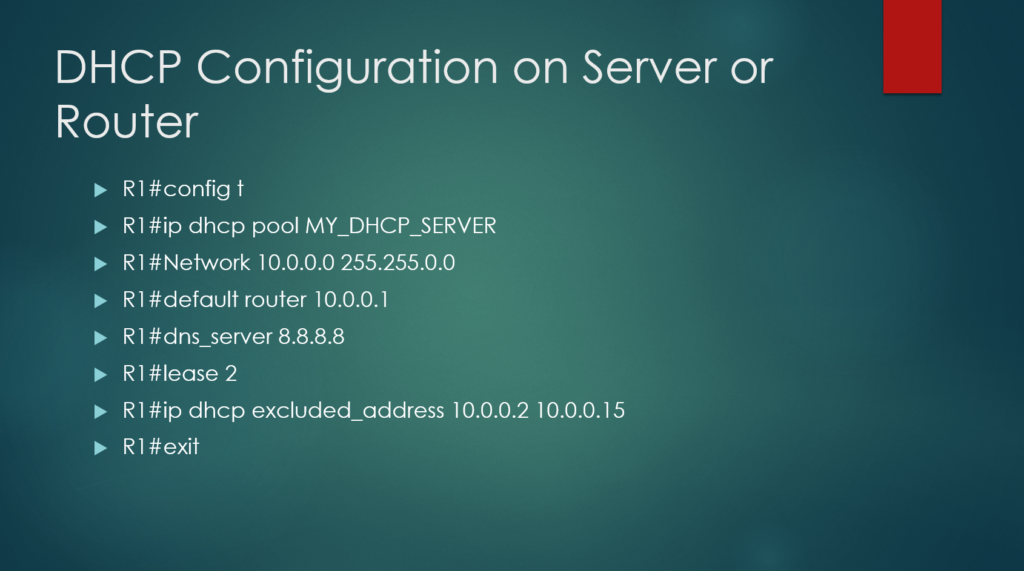
DHCP Configurations:
HOw TO CHECK DHCP IS ENABLED OR NOT IN WINDOWS:

Conclusion
In conclusion, the DHCP protocol serves as a powerful tool for simplifying network configuration in modern computer networks. It eliminates the complexities of manual IP address assignment and ensures efficient utilization of address space. With DHCP, network administrators can dynamically allocate IP addresses and provide updated network parameters to connected devices seamlessly. Additionally, the introduction of DHCPv6 extends its functionality to IPv6 networks. However, it’s crucial to implement proper security measures, such as DHCP snooping, to mitigate potential threats. By leveraging the benefits of DHCP and understanding its security considerations, organizations can streamline their network management processes and enhance overall network efficiency.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: Is DHCP only used for assigning IP addresses?
A: No, DHCP can also provide other network configuration parameters like default gateway and DNS server information.
Q: Can DHCP be used in both small and large networks?
A: Yes, DHCP is scalable and can be implemented in networks of all sizes.
Q: What happens if the DHCP server becomes unavailable?
A: Clients with previously assigned IP addresses can continue to use them until the lease time expires. However, new clients will not be able to obtain IP addresses or network configuration.
Q: Are there any alternatives to DHCP for network configuration?
A: Yes, static IP addressing is an alternative, but it requires manual configuration and lacks the dynamic nature of DHCP.
Q: Can DHCP be used for assigning IPv6 addresses?
A: Yes, DHCPv6 is specifically designed to assign IPv6 addresses and provide network configuration in IPv6 networks. and the range starts from FD00::/7

